ChatGPT-Themed Phishing? Here’s a DIY DRS Guide to IoC Expansion and Threat Discovery
Despite being newly launched, ChatGPT has taken the world by storm. The business community is generally thrilled at what the AI chatbot can do, and threat actors are riding the wave. Phishers have been spoofing ChatGPT to lure people into handing over their credit card information and other sensitive data.
This edition of our DIY investigation guide will demonstrate how organizations can lessen the risks ChatGPT-themed threats pose using different Domain Research Suite (DRS) search and monitoring tools.
Process #1: ChatGPT-Themed Phishing IoC Expansion
As forensic data that hint at possible malicious activities, indicators of compromise (IoCs) are valuable threat intelligence that can lead to more dangerous properties. To illustrate, we mapped out the WHOIS and DNS footprints of chatgpt-openal[.]com—a domain involved in phishing campaigns.
Step #1: Digging Up WHOIS Connections
1. Go to WHOIS Search, type the domain into the search field and click Search.
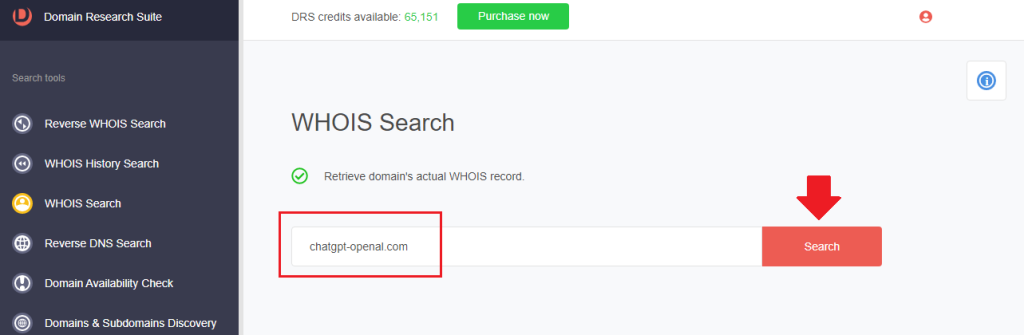
2. Scroll down to the Registrant Contact details.
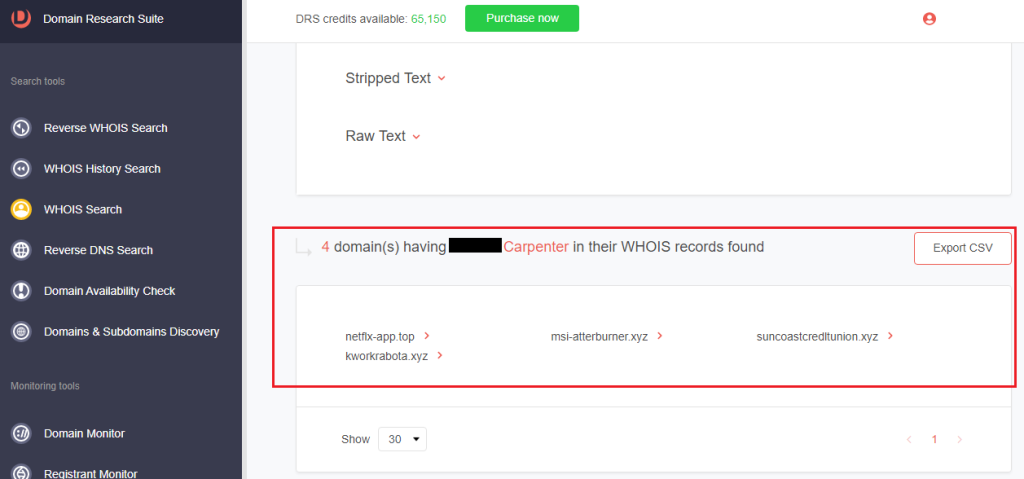
3. Click an unredacted WHOIS field. For chatgpt-openal[.]com, we found an unredacted registrant organization name.
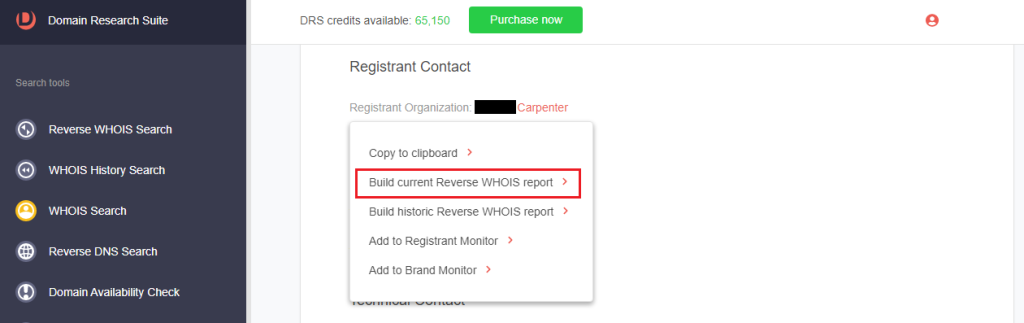
4. Click Build current Reverse WHOIS report. We discovered four other domains registered by the same entity behind the IoC.
Step #2: Mapping Out an IoC’s DNS Footprint
1. Go to Reverse DNS Search and make sure you are on the Obtain connected domains tab.
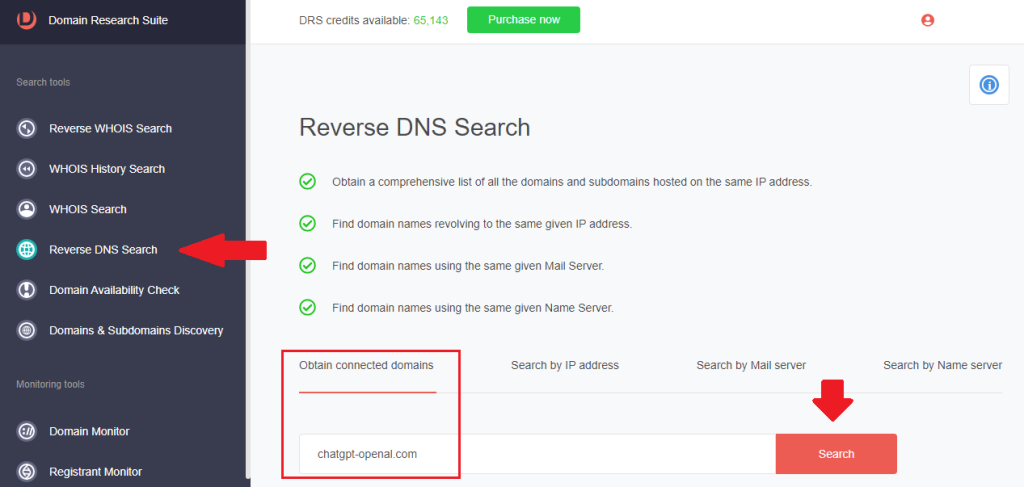
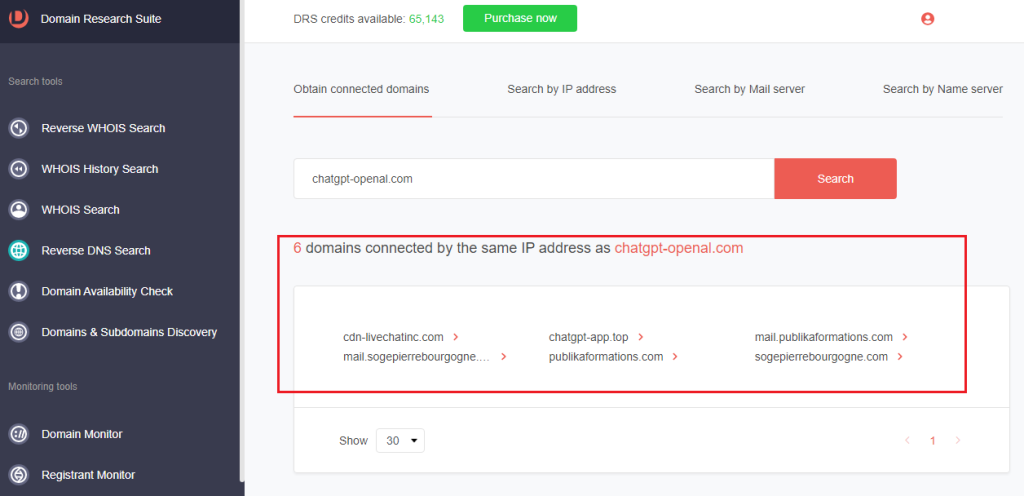
2. Type the domain name into the field and click Search. For chatgpt-openal[.]com, we found six additional domains sharing the same IP host as the IoC, including another ChatGPT look-alike domain.
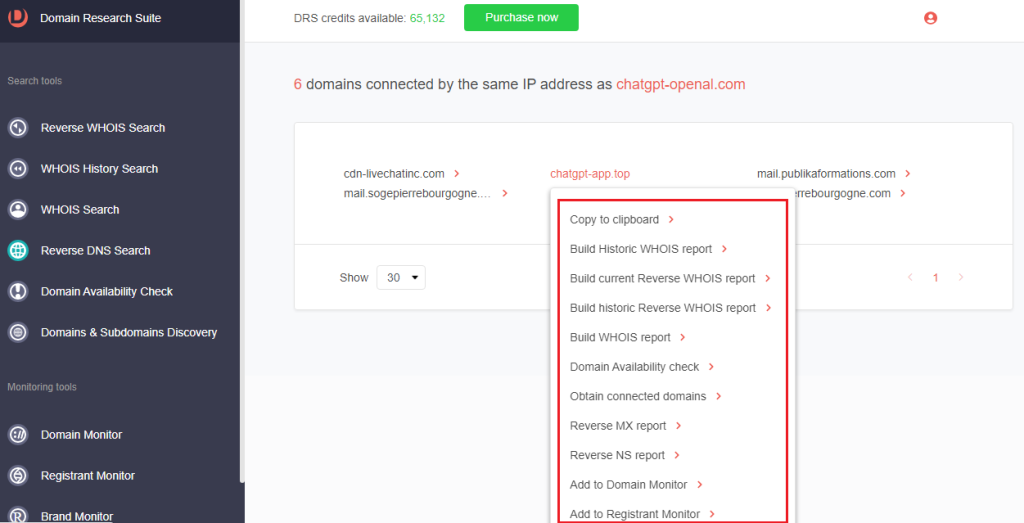
3. [PRO TIP]: You can pivot off any connected domain to obtain its current or historical WHOIS records, check its availability, set up domain and registrant monitoring trackers, and other processes.
Process #2: Domain Attribution
After the IoC expansion, the next step is to determine to which entities the discovered domains belong. We did this through these steps.
1. From Step 2.3 of the IoC expansion process, click a domain and select Build WHOIS report.
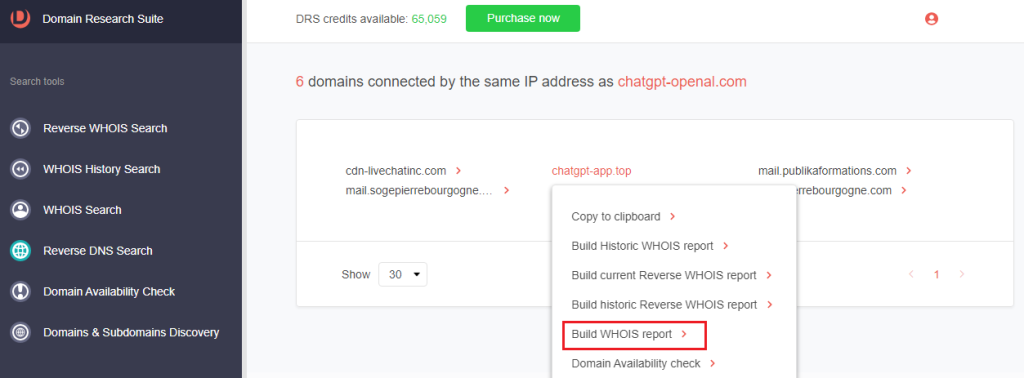
2. Scroll down to check the Website contacts, Web categories, Domain age, Registrant Contact, and other WHOIS details.
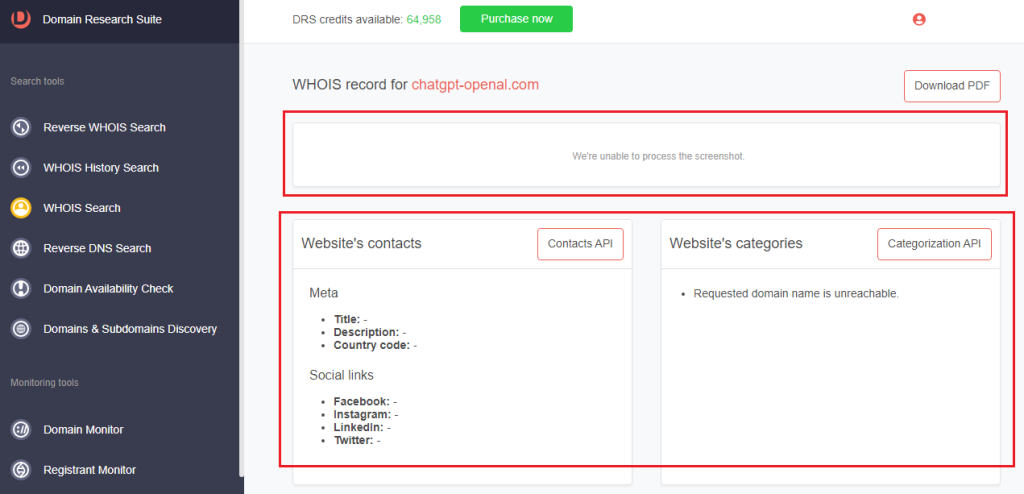
a. Website contacts and categories: These details are blank, and the absence of a website screenshot indicates the domain is not yet resolving.
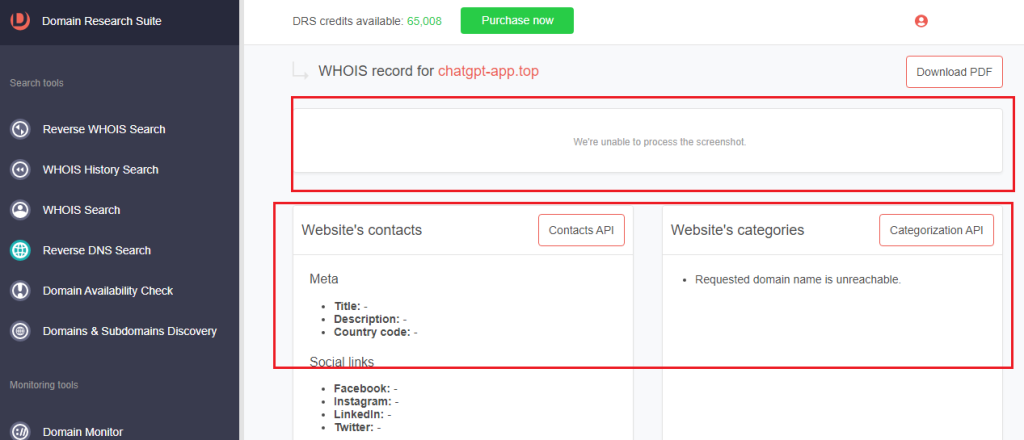
b. Domain age: The domain is barely a month old as of this writing, having been created on February 20th, 2023 only.
c. Registrar name: The domain was registered with NICENIC INTERNATIONAL GROUP CO., LIMITED.
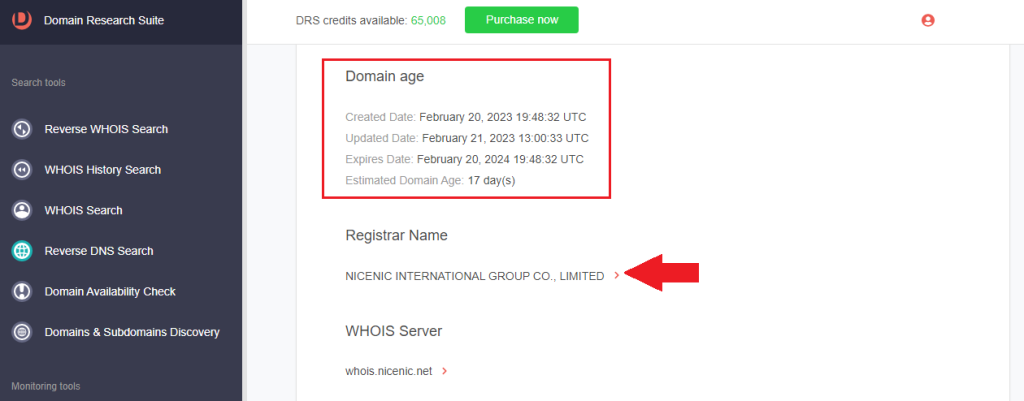
d. Registrant contact details: While the rest of the registrant details are redacted, the registrant organization, state, and country are not.
3. Pull up the IoC’s WHOIS information (chatgpt-openal[.]com in this demonstration) to compare it with the connected domain you found. Go to WHOIS Search, type the domain into the search field and click Search.
4. Scroll down, check the following against the details obtained in Step 1, and note the similarities.
a. Website contacts and categories: As with the connected domain, these details are blank, indicating that the domain is not yet resolving.
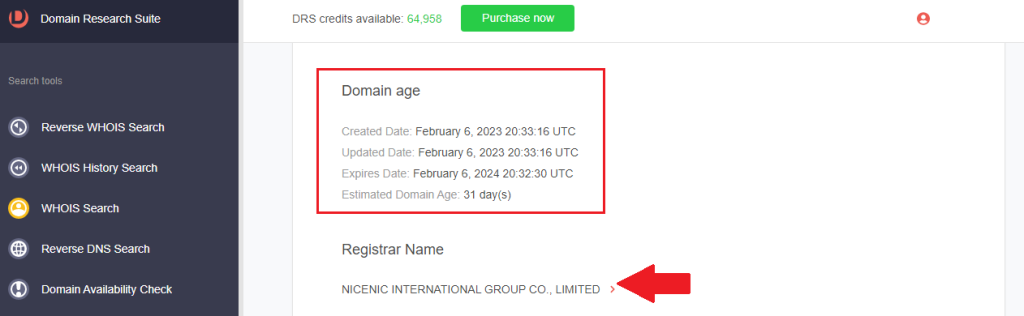
b. Domain age: The domain was registered on February 6th, 2023.
c. Registrar name: The domain was registered with NICENIC INTERNATIONAL GROUP CO., LIMITED.
d. Registrant contact details: While the rest of the registrant details are redacted, the registrant organization, state, and country are not.
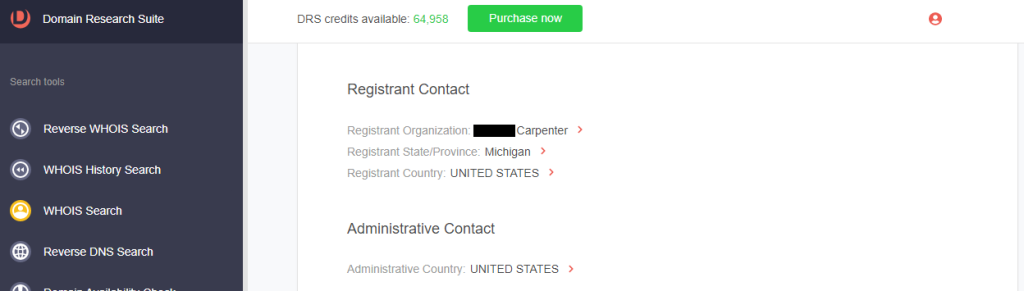
5. Based on similarities in their WHOIS information and the fact that they shared the same IP host, we can potentially attribute chatgpt-app[.]top to the entity behind the malicious domain chatgpt-openal[.]com.
Process #3: ChatGPT-Themed Threat Discovery
You can uncover domains related to a threat in a process called “threat discovery or expansion.” And since ChatGPT-themed phishing is a real threat, we demonstrated how to perform that below.
1. Go to Domains & Subdomains Discovery and type chatgpt as a search string (this would depend on the threat you are investigating).
2. Select the placement of the search string. That can be Starts with, Ends with, Contains, or Exact match.
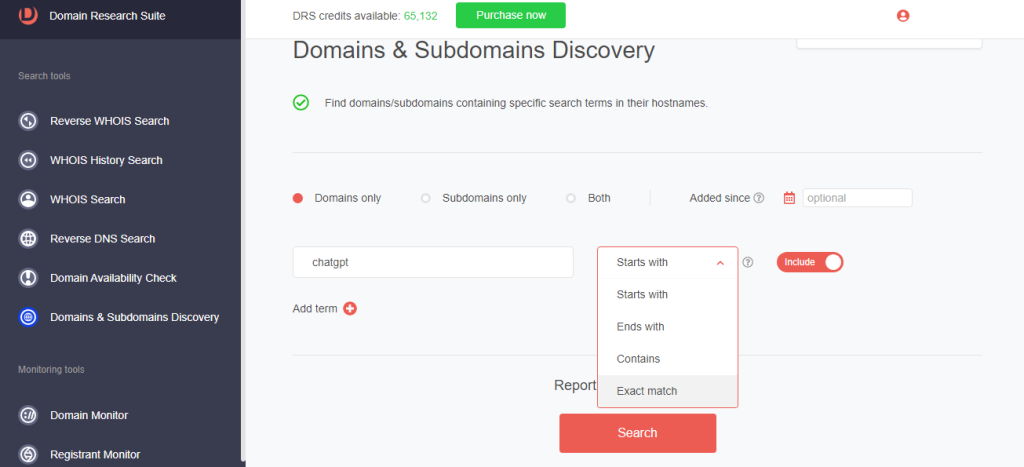
3. Set the Added since parameter if you want to obtain time-bound results. For this illustration, we wanted to retrieve recently added domains, so we set this parameter to February 1st, 2023.
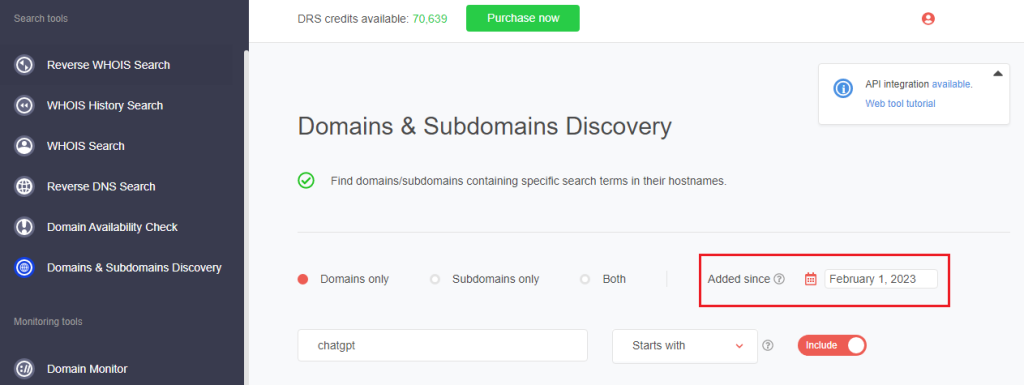
4. Having set the necessary parameters, the tool returned 3,517 domains that started with the string chatgpt registered from February1st, 2023 to March 9th, 2023 (the date of this experiment).
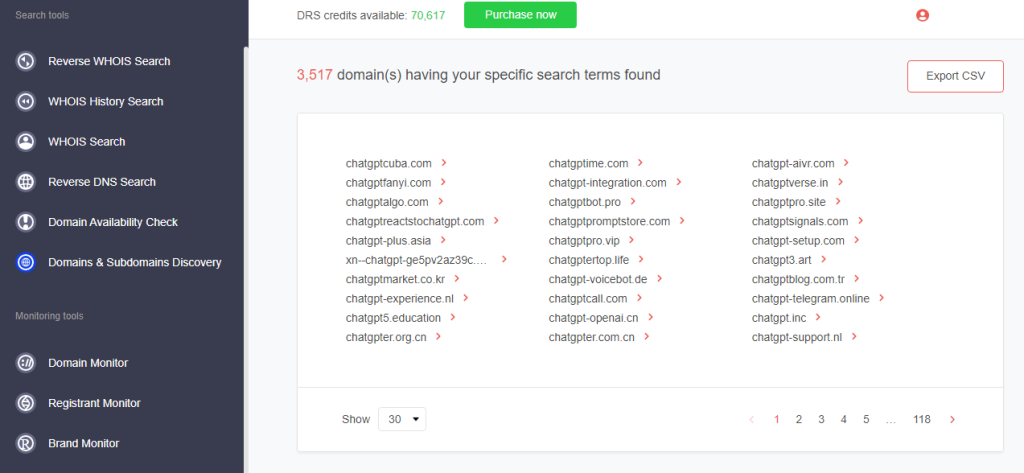
5. [PRO TIP]: Use as many search strings relevant to the threat as possible.
a. For instance, we also performed steps 1–4 using OpenAI as a search string since the company name was also used in phishing campaigns.
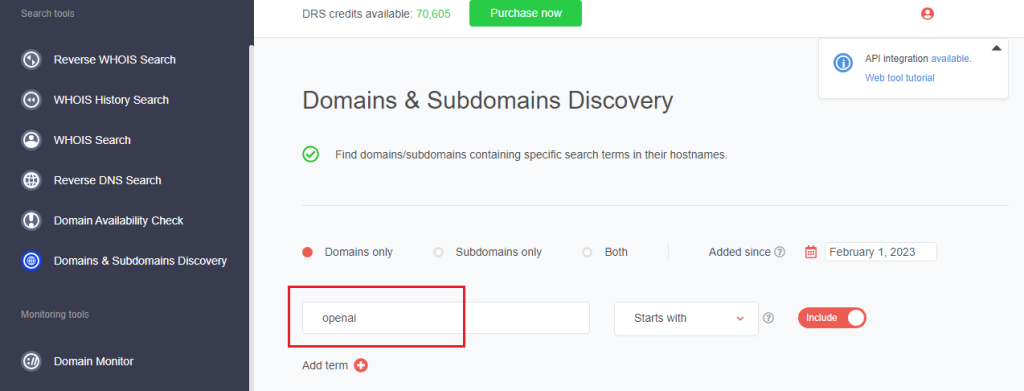
b. We found 773 more domains that could serve as potential vehicles for the threat.
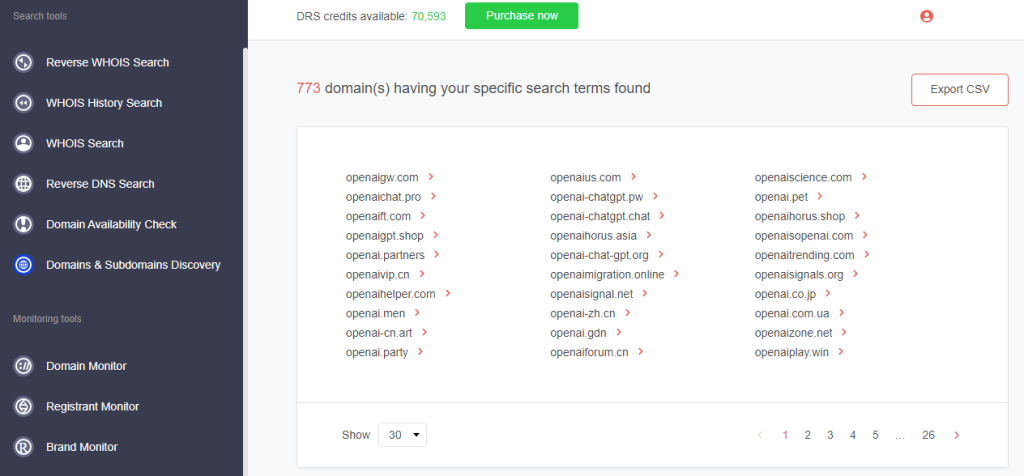
6. On Domains & Subdomains Discovery, click the Subdomains only radio button.
7. Type the search string and set the date and string placement parameters (refer to steps 2 and 3 above).
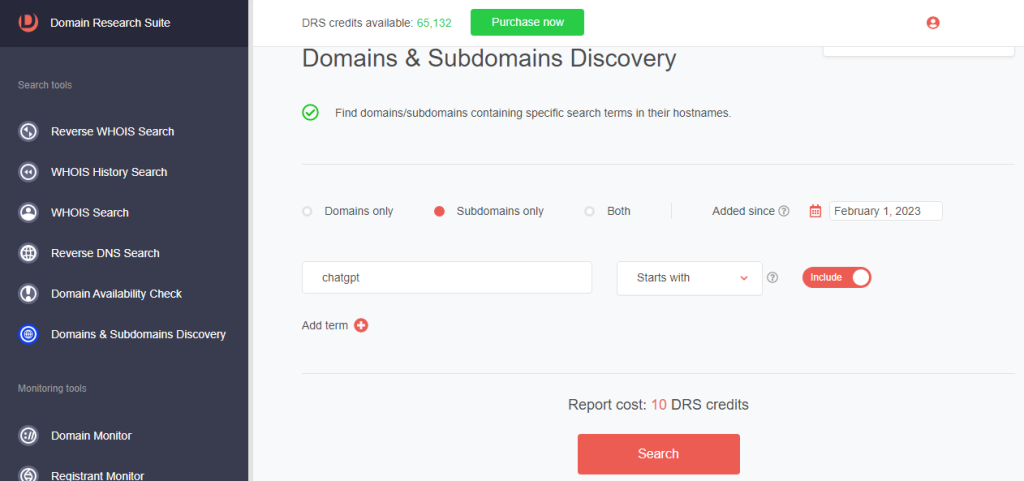
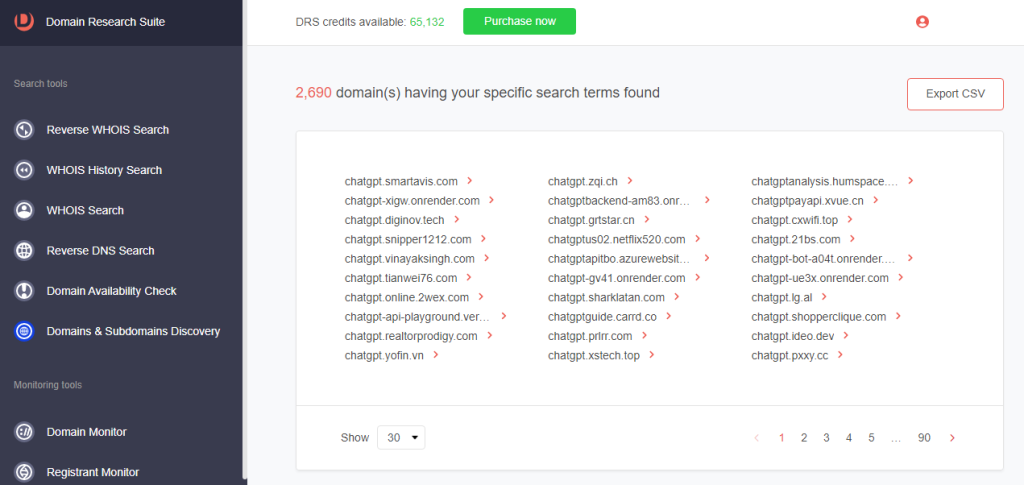
8. Click Search. We found 2,690 subdomains added since February 1st, 2023 that began with chatgpt.
Process #4: Monitoring the DNS for ChatGPT-Themed Domains
Here’s how you can get alerted every time domains bearing a specific brand or company name gets added, updated, or dropped.
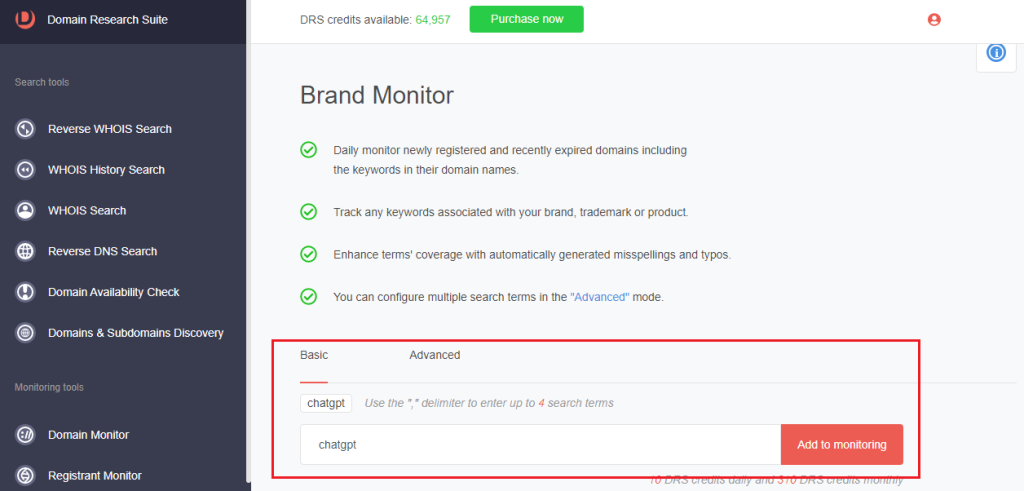
1. Go to Brand Monitor, type a brand, company, or individual’s name and click Add to monitoring. For this illustration, we’re tracking domain registrations related to ChatGPT.
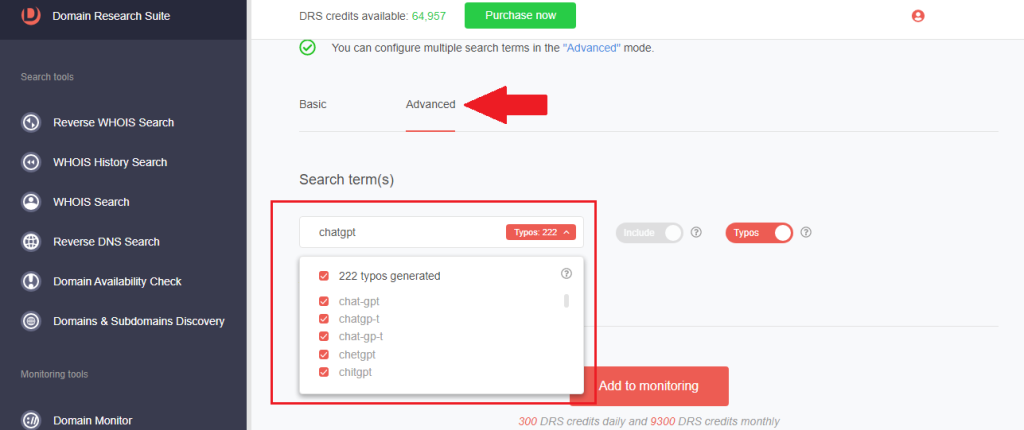
2. [PRO TIP]: Use the Advanced search function to include typo-containing variants of the search term. For chatgpt, the tool detected and tracked 222 typo-containing variants.
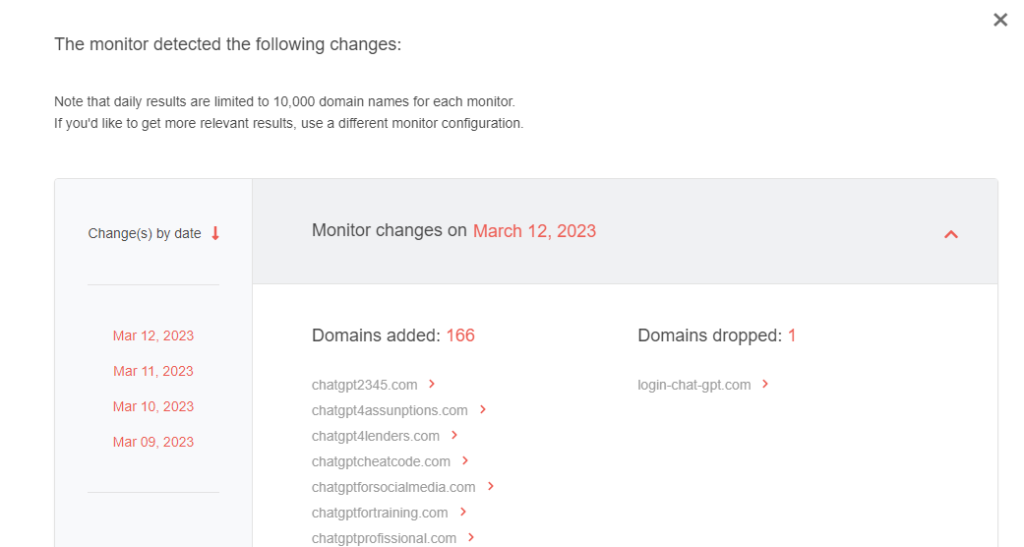
3. Wait for the email alert or recheck Brand Monitor after 24 hours. The tool provides daily results. We noticed an average of 117 registrations per day for the string we monitored.
With threat actors increasingly using the latest technology trends to target victims, cybersecurity processes like IoC expansion, domain attribution, threat discovery, and DNS monitoring are now critical to maintaining an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
In this demonstration, we mapped out thousands of recently added web properties that could serve as potential phishing vehicles. We also detected hundreds of suspicious ChatGPT-containing domains daily.
Are you interested in doing similar fraud investigations? Access DRS if you are an existing user or sign up if you are a first-timer.